The back muscles, a complex and powerful group, play a pivotal role in our daily lives and athletic endeavors. From maintaining proper posture to enabling explosive movements, back muscles are the unsung heroes of our physical well-being.
Delving into the intricate anatomy and physiology of back muscles, we’ll explore their structure, function, and innervation. We’ll uncover the importance of regular back muscle strengthening exercises and provide a comprehensive guide to stretching techniques for flexibility and injury prevention.
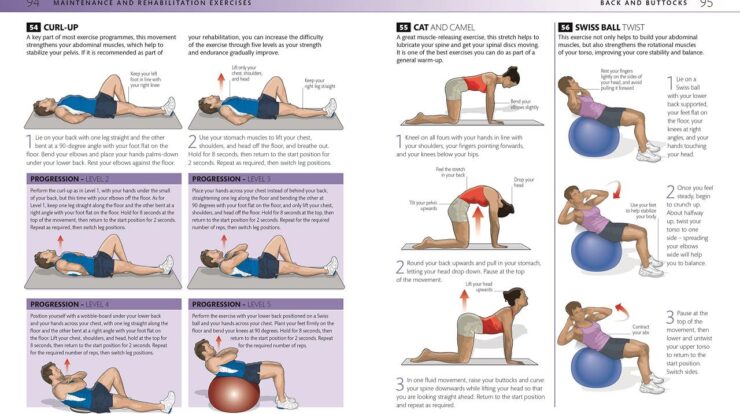
Strengthen your back muscles with these effective exercises you can do at home. Learn more in our guide to Lower Back Exercises at Home .
Back Muscles
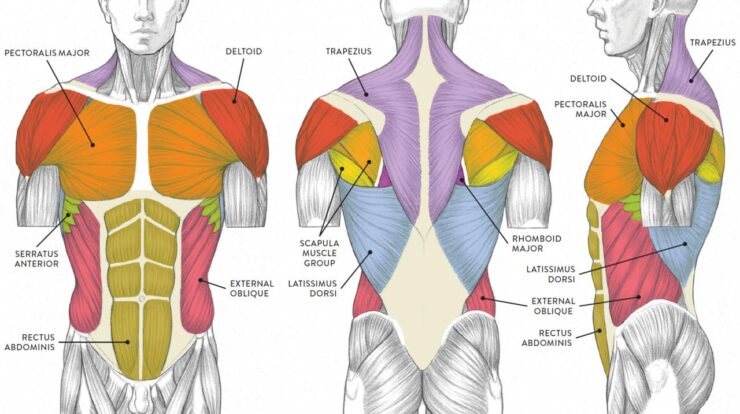
The back muscles, also known as the posterior muscles, are a complex and vital group of muscles that play a crucial role in posture, movement, and stability. These muscles extend from the base of the skull to the pelvis, forming a network that supports the spine and facilitates a wide range of motions.
Show your sister some love on Mother’s Day with a heartfelt message. Check out our Happy Mother’s Day Sis post for inspiration.
Anatomy and Physiology of Back Muscles
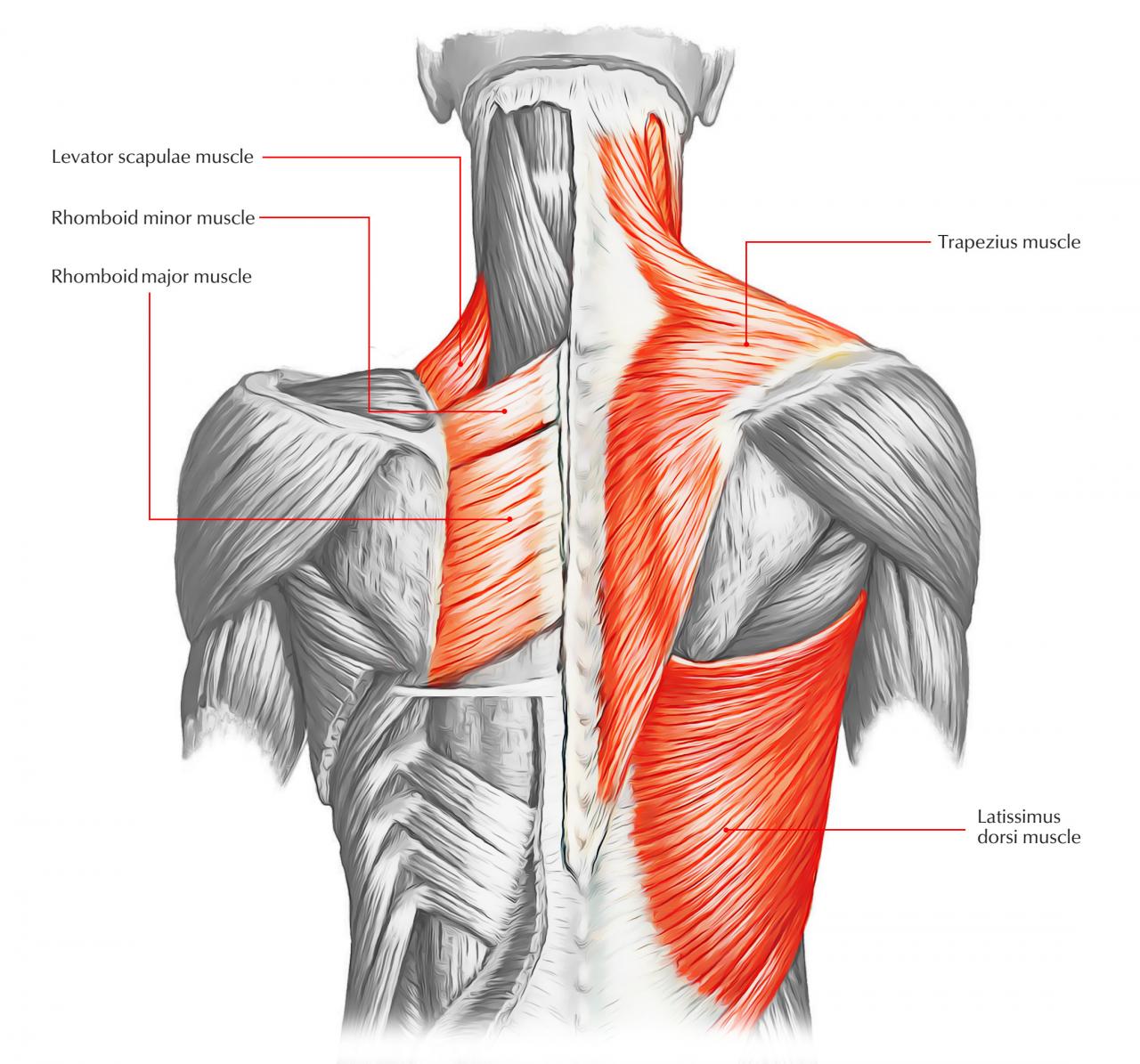
The back muscles can be broadly classified into three layers: superficial, intermediate, and deep. The superficial layer includes the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, and rhomboid muscles. The intermediate layer consists of the erector spinae, which is further divided into three columns: iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis.
Snoop has got the Mother’s Day spirit! Check out the latest Snoop’s Happy Mother’s Day post on social media.
The deep layer comprises the rotatores, multifidus, and interspinales muscles.
These muscles receive innervation from the spinal nerves and are responsible for a variety of movements, including extension, flexion, lateral flexion, and rotation of the spine. They also contribute to scapular movement and shoulder stability.
Exercises for Strengthening Back Muscles
- Pull-ups:Engage the latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, and biceps.
- Barbell rows:Target the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, and erector spinae.
- Deadlifts:Work the erector spinae, glutes, and hamstrings.
- Planks:Strengthen the erector spinae, rectus abdominis, and obliques.
- Back extensions:Isolate the erector spinae and improve posture.
Regularly performing these exercises helps build strength, enhance posture, and reduce the risk of back pain.
Stretches for Back Muscles
- Cat-cow stretch:Improves spinal flexibility and relieves tension in the erector spinae.
- Child’s pose:Stretches the latissimus dorsi and rhomboids.
- Standing quad stretch:Lengthens the erector spinae and hamstrings.
- Hamstring stretch:Enhances flexibility in the erector spinae and hamstrings.
- Seated spinal twist:Improves rotational mobility and reduces stiffness in the back muscles.
Incorporating these stretches into a regular routine promotes flexibility, reduces muscle imbalances, and prevents injuries.
Common Back Muscle Injuries
- Muscle strains:Overstretching or tearing of muscle fibers, often caused by improper lifting or sudden movements.
- Muscle sprains:Ligament injuries resulting from overextension or twisting.
- Herniated discs:Bulges or tears in the intervertebral discs that can compress nerves and cause pain.
Seeking medical attention for back injuries is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Expecting moms can also celebrate Mother’s Day! Let’s discuss the etiquette of wishing Happy Mother’s Day to a pregnant woman .
Role of Back Muscles in Sports and Fitness
Strong back muscles are essential for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. They contribute to:
- Power and speed:Explosive movements such as sprinting and jumping require powerful back muscles.
- Stability and balance:Back muscles stabilize the spine during dynamic activities like running and weightlifting.
- Injury prevention:Well-developed back muscles protect the spine and reduce the risk of injuries.
Nutritional Support for Back Muscle Health
Maintaining healthy back muscles requires adequate protein, carbohydrates, and other nutrients. Protein is essential for muscle growth and repair, while carbohydrates provide energy for muscle contractions. Other nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and potassium support muscle function and recovery.
Closing Notes
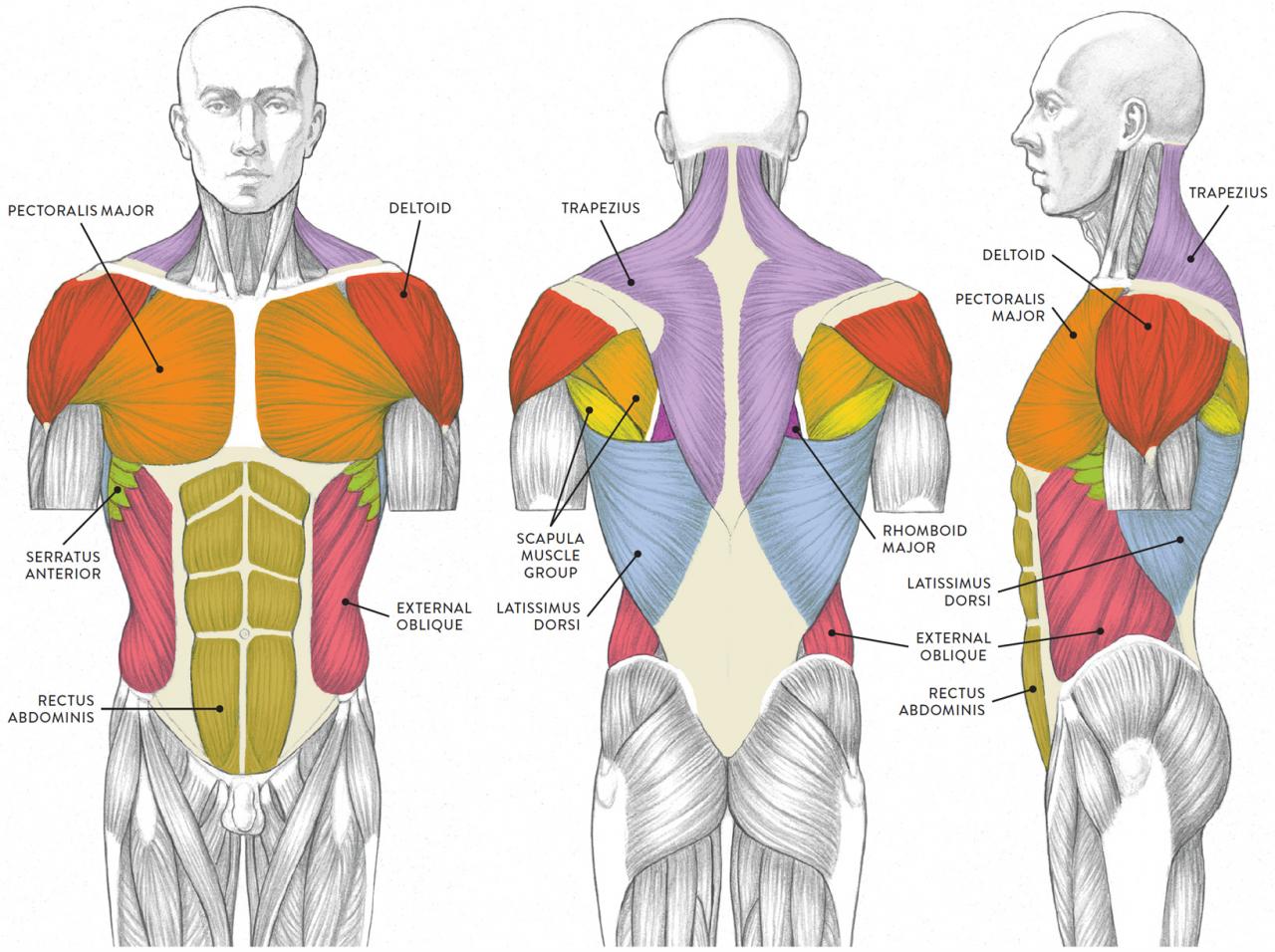
In conclusion, back muscles are essential for overall health and fitness. By understanding their anatomy, engaging in targeted exercises, and incorporating proper nutrition, we can unlock their full potential, enhancing our posture, improving our performance, and reducing the risk of injuries.
Popular Questions
What are the most common types of back muscle injuries?
Strains, sprains, and tears are the most prevalent back muscle injuries.
How can I prevent back muscle injuries?
Proper exercise technique, maintaining good posture, and avoiding excessive strain can help prevent back muscle injuries.
What are the benefits of stretching back muscles?
Stretching back muscles improves flexibility, reduces muscle tension, and prevents injuries.